Izotope Rx 7 Dereverb
- Izotope
- Izotope Rx 7 De Reverb 2017
- Izotope Rx7 De Reverb
- Rx7 De Reverb
- Izotope De Reverb
- Izotope Rx 7 Dereverb Review
- Izotope Rx 7 De Reverb 1
De-reverb
De-reverb gives you control over the amount of ambient space captured in a recording. It can make large cathedrals sound like small halls and make roomy vocals sound like they were recorded in a treated space.
Reverb is the ambient sound of audio energy as it loses power in a space. We can think of a sound in a room as having two components: the direct sound and its reverberant tail. The reverberant tail decays in power over time depending on various factors, like the size of the space, the materials in it, and the geometry of its construction.
- Sep 13, 2018 Today's video is about the new Izotope RX. I discuss some of its newest features such as Repair Assistant, Music Rebalance, and Find Similar.
- Mar 06, 2019 IZotope RX 7 Audio Editor Advanced 7 Download Free is Powerful software for audio restoration product on the market, IZotope RX 7 Free Download is most software for Noise Reduction & Audio Repair, now you can download from Download-Plus.com with a direct download single link with fast speed dedicated server.
- The revolutionary new Dialogue Match, mixing powerhouse Neutron 3 Advanced, and impeccable Stratus 3D and Symphony 3D reverbs join RX 7 Advanced, Insight 2, and RX Loudness Control to bring you the most comprehensive post production software package on earth.
RX 7 Standard is the audio repair toolkit used on albums, movies, and TV shows to restore damaged, noisy audio to pristine condition. View More Add to Cart. De-reverb Reduce some of the reverb from a recorded space with the De-reverb audio plug-in and module in iZotope RX 7. Salvage recordings of dialogue containing too much reverb/acoustic space without needing to spend time/money on a reshoot or ADR.
Reverb tails also have an important time component: early reflections. Early reflections are the rapid echoes of a direct sound from a nearby surface. They are often distinct from the rest of a reverberant tail because they have a lot of energy but end quickly. Early reflections typically comprise the first 5 to 100 milliseconds of a reverb tail.
If a listener (or a microphone) is close to the source of a direct sound, the direct sound is perceived more than the reverb. If a listener is farther away from a direct sound, more reverb is perceived in relation to the direct sound. A listener moving away from the direct sound in a space will eventually cross a threshold where the reverberant signal is perceived as prominently as the direct signal.
De-reverb processes audio according to the reverberant/direct ratio (also known as wet/dry ratio) detected in the signal. It can learn your audio to suggest some frequency and decay time settings, or you can estimate these yourself.
De-reverb has the effect of sharpening a signal in time. You can notice this transition in the spectrogram: reverberant audio looks blurred, and cleaned audio appears more focused. Here, a recording of a distant speaker (left) has had its long tails processed (center) before another De-reverb pass with shorter tail lengths to tackle the early reflections (right).
Learning a Reverb Profile
To find the best settings for your signal quickly, find about five seconds of audio that starts with noise and has both direct signal and reverberant tails.
Izotope
RX De-reverb can suggest some settings based on your signal.
Find five to ten seconds of audio that starts with noise and has both a direct signal and a reverberant tail.
Direct signal, reverberant tail, and noise are all important to help De-reverb understand your audio and set its controls appropriately. It needs to understand the ratio of dry signal to reverberant signal, how long reverb tails last, and where the noise floor of your signal is (to avoid excessive processing).
If you are having trouble finding a good portion of audio to help De-reverb learn a good reverb profile, try running the Learn feature on any transient audio where both the direct signal and reverberant tail are apparent.
Complicated Reverbs
If the audio you are working with has a very complex reverb, such as a reverb with apparent early reflections, you may get better results after trying a few passes of De-reverb.
First, start by training the De-reverb and set the Reduction amount to a value that yields good results on the long reverberant tail. After processing, Learn a new reverb profile and try reducing the level of early reflections: set the Tail Length control to 0.5, Artifact Smoothing around 3.0, and increase Reduction.
A combination of De-reverb and De-noise can be used to tame very reverberant signals. It does not matter whether you process with De-reverb or De-noise first.
De-reverb Controls
Learn
Teaches De-reverb how much reverb is in your signal.
The Learn feature analyzes the signal and determines the wet/dry ratio per frequency of your signal, as well as the overall rate of decay of reverb.
When the Learn operation completes, the Reverb Profile and Tail Length controls will be set to their suggested values.
The Learn operation can be performed on any reverberant audio. We strongly recommend using the Learn feature on a selection of audio that starts with some noise floor (or room tone), is several seconds long, and includes both the direct signal and its reverberant tails.
Try to find a good five second slice of reverberant audio. If you can find enough direct signal and reverberant tails to fill the De-reverb signal trace meter while using Learn, you will probably get a good reverb profile.
If you have trouble getting good results from using the Learn feature, you can try
- learning on transient broadband audio, like drums, claps, or coughs;
- learning on any audio that is obviously reverberant; and
- learning for a longer amount of time — most reverb can be analyzed in a few seconds, but some reverb profiles can require up to ten seconds of analysis.
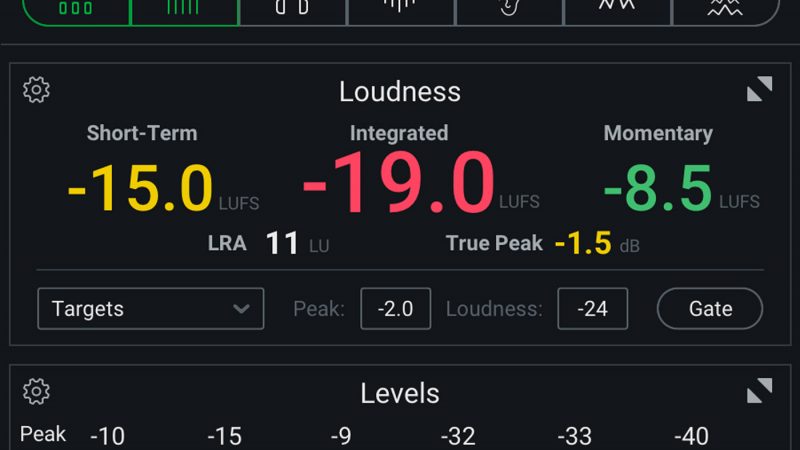
Metering
The top meter shows a comparison between the input and output signal energy over the past five seconds of playback.
The bottom meter shows the amount of reverb reduction over time. It is the difference between input and output plotted on a flat line.
Both of the meters together give you an idea of what De-reverb considers reverb and help you refine your settings.
Reduction
Controls the amount of De-reverb effect applied.
Larger amounts mean more reverb is removed. Smaller amounts perform less processing.
This control represents the target wet/dry ratio for processing. In other words, if it is set very high, it will treat the signal as though it has more reverb and process it more.
If the output of De-reverb sounds unnatural after Learning, try slowly turning this control down first.
Negative reduction will increase the amount of reverb in the signal.
Reverb Profile
Izotope Rx 7 De Reverb 2017
Controls the amount of De-reverb effect applied per band. Thesecontrols are set automatically by the Learnfeature.
If a group of reverberant tones are more prominent in a signal, increase the control for that band.
Generally you want to set these controls to match the reverb originally present in your signal. For example, if reverb takes longer to decay (or is more present) in a particular band, set that control higher.
These controls can also be used to address more prominent ringing or resonant groups in signals. For example, increasing the profile control for low frequencies can remove muddiness from a resonant bass guitar, while increasing the high band control can curtail ringing sibilance in live vocal recordings.
Tail length
Controls the decay of De-reverb processing.
This control is an approximation of RT-60, the rate of time it takes for a reverberant signal to decrease in amplitude by 60 dB.
This is automatically set by the Learn feature.
Increase this control if reverb tails reappear after processing, or if early reflections are too apparent.
Djay pro 2 spotify record. Logo-djay-school DJ School Logo Learn to DJ and sharpen your skillsAlgoriddim teamed up with the most talented DJs to teach you the art of mixing music.
Decrease this control if reverb tails and noise floors sound over-processed, or if the processed audio sounds dull.
This control can be set to its minimum setting to process early reflections.
Artifact smoothing
Controls the frequency accuracy of De-reverb processing.
Because reverb is generally smooth across the frequency spectrum, the default value of this control is very high. However, if you need more accuracy to address issues like resonant tones in a room, you can decrease this control. The tradeoff is generally more artifacts from strong processing, so you may have to balance adjusting this and the Reduction control.
Enhance dry signal
Increases the level of the direct signal.
Boosting the non-reverberant signal can help create more dynamic range in the signal and is a good option to try when working with voice or transient material. Enabling Enhance Dry Signal can also help prepare material for later de-noising.
Output reverb only
Changes the output of De-reverb from the processed signal to the wet reverberant signal.
This is useful for monitoring the processing to get better results. Hearing just the reverb helps you understand the impact of controls like Reduction, Reverb Profile, Tail Length, and Artifact Smoothing.
When this option is enabled, the output may not sound much like reverb because it is the difference of processing against the original signal, with some enhancement to expose more of the reverb apparent in the recording.
Using De-reverb as a real-time plug-in
De-reverb is available as a VST/AU/RTAS/AAX real-time plug-in inside your DAW or NLE. However, due to the complexity of this processing, it can be resource intensive. To achieve high-quality results, it is always best to bring the audio file in question into RX Editor (via RX Connect or by opening it directly), applying De-reverb, and then returning the file back to your original session.
iZotope RX 7 Audio Editor Advanced v7.01 VST AU AAX
Size WIN/OSX 322 Mb/855 Mb
RX 7 The industry standard for audio repair
As the industry leader in audio repair, RX 7 introduces Repair Assistant and Music Rebalance, plus tools for any audio post production job.
The gold standard for post production engineers everywhere
RX 7 leverages cutting-edge machine learning technology for unparalleled audio quality.
Designed specifically for the demanding needs of post production professionals, RX 7 Advanced introduces brand new processing powered by machine learning, powerful AudioSuite tools, and multichannel support up to 7.1.2.
Restore the intended performance
With the new Dialogue Contour module, you can reshape the intonation of dialogue to rescue or improve a performance in post production. Dialogue Contour features pitch correction processing that is tailored to speech and designed to adjust the inflection of words within a phrase of dialogue that may not match or flow correctly with the rest of the dialogue in the clip. Easily splice together natural-sounding sentences or turn statements into questions!
Izotope Rx7 De Reverb
New plug-ins, new workflows
Rx7 De Reverb
Time is everything, and we’ve added even more AudioSuite plug-ins to RX 7 Advanced to help you get more of it back. User-favorites Dialog Isolate and De-rustle are now also available in Pro Tools AudioSuite, giving you even more flexibility in your audio repair workflow. Plus, RX 7 Advanced now lets you repair multichannel audio up to 7.1.2 Dolby Atmos.
Izotope De Reverb
Why RX 7?
Easy vocal reshaping
Quickly reshape your performer’s intonation with Dialogue Contour, allowing you to save or improve a performance in post.
Crystal clear dialogue
Tools like Dialogue Isolate and Dialogue De-reverb ensure that your audience catches every word with perfect clarity.
Professional surround support
With support through Atmos 7.1.2, RX 7 is ready to take on post production jobs in almost any professional multichannel format.
RX 7 Features
Izotope Rx 7 Dereverb Review
Repair Assistant
Audio spot-cleaning in seconds
Post production is all about getting as much done in as little time as possible. Repair Assistant is an intelligent repair tool that can detect noise, clipping, clicks, and more. Solve common audio issues faster than ever by selecting the type of material (music, dialogue, other) and letting Repair Assistant analyze the audio with one listen.
Music Rebalance
Music Rebalance is a powerful tool that intelligently identifies vocals, bass, percussion, and other instruments in a mix for fast, independent gain adjustments.
Dialogue Contour
Using Dialogue Contour, you can now reshape the intonation of dialogue to rescue or improve a performance in post production—no ADR session time required!
Dialogue De-reverb
Reduce or remove unwanted reverb from dialogue clips using algorithms trained with machine learning and optimized to separate spoken dialogue from reverberance.
Version 7.01 Release Notes:
Changes/fixes :
– New “Prevent Clipping” export option: Predicts and prevents clipping when exporting to OGG & MP3 file formats in the RX Audio Editor.
– Mouth De-click Processing Improvements: Improved – Mouth De-click results for Japanese dialogue.
– Improved processing time when using RX Connect for – Direct Offline Processing in Nuendo.
– Fixed file length discrepancies that could occur when encoding or decoding mp3 files.
– Fixed erroneous clipping detection in the Repair Assistant module.
– Improved offline processing time of the Spectral De-noise module.
– Improved performance when processing multiple file tabs with Mouth De-click in the RX Audio Editor.
– Improved processing quality in the Dialogue Isolate module.
– Various bug fixes.